Many newcomers to the cryptocurrency industry often learn about Bitcoin first and then Ethereum. The reason is not far-fetched. Ethereum is the second most successful cryptocurrency-based project after Bitcoin (BTC), as evidenced by its large market capitalization.
Additionally, Ethereum publicized the innovative idea of enabling user-focused applications on a decentralized network. This opened up a whole new world of possibilities that is still being explored by the thousands of blockchain networks that have been launched over the past decade since the Ethereum network went live in 2015.
Let’s dive deeper into the network and its native currency, Ether (ETH). As we do, you will learn a brief history of the blockchain, how it works, the applications it powers, and much more. Whether you are a seasoned crypto user or someone just starting to learn about cryptocurrencies, this article is for you.
A Brief History of Ethereum
Ethereum emerged in the wake of the Bitcoin revolution. A Russian-Canadian programmer, Vitalik Buterin, initially conceived the idea in late 2013 in a whitepaper describing a way to build decentralized applications.
However, it was not until nearly two years later, with support from other founders, that Ethereum became a reality. In addition to human resources, Ethereum’s developers raised $16 million through an initial coin offering (ICO), a record-breaking figure at the time.
The network eventually launched in July 2015, becoming one of the first decentralized networks to consider blockchain technology’s full potential beyond enabling a secure virtual payment method.
Other Ethereum co-founders include Gavin Wood, Charles Hoskinson, Amir Chetrit, Anthony Di Iorio, Jeffrey Wilcke, Joseph Lubin, and Mihai Alisie. Some of Ethereum’s co-founders have moved on to found other crypto projects, notably Charles Hoskinson (Cardano) and Gavin Wood (Polkadot).
Ethereum Explained
Ethereum is a blockchain network just like Bitcoin, which means it allows value to be moved from one part of the world to another without the need for a central entity to confirm or validate transactions. However, Ethereum is a little more than that.
The Ethereum network can be thought of as a computer that allows anyone to use applications or software created by other people or even create their own. In this case, however, instead of everyone having their individual computer, all these applications run on a single computer (the global Ethereum network). Then, anyone who has an Ethereum wallet can connect to these applications and use them.
While this idea may seem abstract at first, it brings immense benefits. For one thing, individuals could finally create applications that run on a single and decentralized “operating system,” not monopolized by any one company, such as Microsoft or Google.
Additionally, with functionalities, such as tokenization, enabled by so-called “smart contracts,” developers could create unique applications. For instance, they can create blockchain-based tokens that represent various types of information, from passwords and personal data to finances, real estate, and debt.
How Ethereum Works
The Ethereum network’s fundamental design is similar to most blockchains. It provides a decentralized, distributed public ledger where transactions are verified and recorded. The network is not operated or managed by any centralized entity.
Instead, it is managed by a global community of users who store an identical copy of this ledger on their computer. This ledger allows them to see all past transactions and is extended as each new block is added to the chain.
Meanwhile, the network uses a consensus model called Proof-of-Stake (PoS). This allows for a specific category of users called validators. These persons lock up a specific amount of ETH for the right to verify and confirm transactions that users perform on the network.
Enough validators must demonstrate that they all had the same comparative results, and the block becomes finalized. Note that the work done by validators is automated and done with the aid of computers, and thus, it does not require someone to sit and verify transactions.
Validators receive new Ether (ETH) coins in exchange for their work and locked assets. Thus, this work-reward mechanism allows new coins to enter circulation while ensuring that the network remains secure.
At this point, it is worth mentioning that since September 15, 2022, when Ethereum fully moved from a Proof-of-work (PoW) to a PoS model, the network slightly differs from other blockchains by adopting what its developers call the consensus layer and the execution layer.
The consensus layer, a.k.a. Beacon chain, is where validators agree on the order of transactions, while the execution layer is essentially where token transfers and smart contract transactions are executed. These two closely knit layers form the Ethereum blockchain as it is known today.
Difference Between Ether and Ethereum
Ethereum and ether (ETH) are terms used for the ether digital currency, but they’re not quite the same thing. Understanding the distinction is an important aspect of navigating the network.
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables developers to create decentralized applications (DApps) utilizing blockchain technology, while Ether (ETH) is the native currency used to power transactions and smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
In essence, Ethereum is the platform, and Ether is the fuel that runs it. Ether is used to pay for on-chain Ethereum transactions but can also be used as an investment, off-Ethereum payment method, or for trading on other crypto exchanges. It is also used as the primary currency to access the thousands of applications currently running on the network.
Industries Where Ethereum Finds Application
Here are a few sectors that benefit from the idea of a blockchain network such as Ethereum:
Finance
The application of Blockchain technology in finance allows users to connect with other users and make transactions directly on a network instead of going through a traditional bank.
Some applications built on the Ethereum blockchain (e.g. Uniswap) allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without the need for a central entity, such as an exchange like Binance or even a bank.
Other kinds of applications (e.g., Compound) allow users to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest on their assets. Imagine being able to buy or sell your assets or secure a loan at any time, even in the middle of the night.
The invention of the Ethereum network originally made all of these possible; little wonder Ethereum’s decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem is valued at around $50 billion, way more than any other blockchain.
Gaming
The Ethereum network led to a new era of games (such as Axie Infinity and Decentraland) that allow users to earn crypto rewards for gameplay. Users can also own the assets they use for the game and can trade them in a decentralized manner.
This new experience makes games more profitable for players who spend so much time and money playing. The blockchain gaming industry is valued at over $26 billion and has attracted the attention of some of the world’s biggest gaming studios, including Sony and Epic Games.
Governance
Governance is another field of human endeavor that has gotten a lift with the advent of Ethereum. These days, many online communities called decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have sprung up.
Thanks to the power of the blockchain, members can pool resources to achieve common goals, such as investing in startups or supporting humanitarian efforts. Other kinds of DAOs use smart contracts to enable members to make community decisions, the more reason many proponents believe DAOs could become the primary governance model for internet primitives.
With knowledge of some of the applications powered by Ethereum, it is time to examine more closely how this “global supercomputer” compares and differs from its predecessor, Bitcoin.
Ethereum vs Bitcoin
At the time of writing, Bitcoin is currently valued at more than four times the value of Ethereum. Nonetheless, both networks have some similarities and differences that investors should know, especially when considering whether or not to invest in them.
Ether vs. Bitcoin Similarities
- Decentralization: Both Ethereum and Bitcoin run on blockchain technology, with a major focus on decentralization. No central institution or authority regulates them.
- Widespread Adoption: These two cryptocurrencies are considered very valuable thanks to their widespread network adoption. Ethereum has a very active group of users interacting with the many decentralized applications on the network. Bitcoin adoption is more institutional but equally as important.
Many financial experts have described both assets as the future of currency, adding that they represent a new financial frontier.
- Volatility: Both cryptocurrencies are extremely volatile. However, Ethereum is considered more volatile than Bitcoin, largely because of its smaller market valuation. The more valuable an asset becomes, the less susceptible it becomes to wild fluctuations.
- Digital Asset: Ethereum and Bitcoin are digital currencies. They can be bought and sold on cryptocurrency exchanges or directly from peers and kept in virtual wallets. No physical copies of the coins exist.
- Economic Value Creation: Thanks to preprogrammed code, miners (on Bitcoin) or validators (on Ethereum) serve as a channel for new coins to come into circulation, thus managing the creation of value on each network.
Ether vs. Bitcoin Differences
- Bitcoin came first: The Bitcoin network launched in early 2009, whereas Ethereum came later, in 2015.
- Ultimate goal: Bitcoin (the currency) has grown to become primarily a store of value assets while Ethereum is functional. Created as an alternative to traditional currencies, Bitcoin aims to be a medium of exchange and store of value. On the other hand, Ethereum offers both decentralized currency and a platform for users to develop protocols and applications.
- Founders: Bitcoin’s founder is currently anonymous and might continue to be so. Its famous whitepaper is credited to Satoshi Nakamoto, but that’s just a pseudonym that could refer to one or several people. So, it’s all a bit of a mystery.
However, we know who founded Ethereum. Several different people are credited with founding Ethereum, but its conceptualization is credited to programmer Vitalik Buterin. Further, the Ethereum project is still mainly managed by the Ethereum Foundation, while Bitcoin continues to benefit from a largely independent and decentralized community.
- Number of coins: The maximum number of bitcoins that can enter circulation is 21 million. Conversely, there can be an unlimited amount of Ether, even though the amount of time it takes to process ETH adds some logistical limits.
- Transaction fees: Another significant difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin is how the respective networks treat transaction processing fees. The fees associated with Bitcoin transactions are paid to Bitcoin miners. On Ethereum, around 90% of the transaction fee, called the base fee, is burned (removed from circulation), while only around 10% goes to validators. Ethereum’s burning mechanism is designed to lower inflation, a problem that Bitcoin solves by using a fixed supply mode.
- Consensus algorithm: Bitcoin uses the energy-intensive proof-of-work (PoW) consensus, which requires miners to compete for rewards, while Ethereum uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Challenges Facing Ethereum
While Ethereum has grown dramatically in years, the blockchain still faces some challenges.
- Problems with Smart Contracts
While smart contracts have been a fantastic innovation, as they have the potential to automate and streamline various processes, unfortunately, they are not foolproof. This means smart contracts can be vulnerable to coding errors, bugs, and even security breaches. This can lead to legal disputes and financial losses.
Another drawback of Ethereum is that smart contracts are not flexible. Once they are deployed on the blockchain, they can not be changed. This becomes even more problematic when a vulnerability is discovered in the agreements, as it becomes difficult to update or fix the contract.
- Scalability Issues
Although Ethereum’s upgrades over the years have aimed to solve the scalability issue, the Ethereum blockchain continues to experience some performance issues. This is a significant problem, especially since decentralized applications require low-cost and fast transactions to remain attractive to users.
Admittedly, Ethereum developers continue to work on implementing new solutions to address the scalability issue. Sharding and layer-2 networks are two of the most prominent methods being used by Ethereum developers to scale the blockchain
- High Gas Fees
Network congestion on the Ethereum Blockchain leads to higher gas fees—a significant factor influencing investing in gas fees. Since the Ethereum gas fee is high, many investors often consider other cheaper options. The outflow of investors can drive down the price of ETH, which might harm your investment. Moreso, when other options offer lower fees for similar applications.
- Interchain Communication and Interoperability
Interchain communications and interoperability are other challenges for Ethereum. Because the blockchain ecosystem continues to expand, there is an imminent need for blockchains to interact and seamlessly communicate with each other. This is crucial for the blockchain industry’s overall growth and decentralized finance (DeFi) development.
- High Volatility
Like every other cryptocurrency, Ethereum is volatile. While this nature allows investors to earn massive rewards, it can also swing the other way. Hence, it is advisable to conduct due diligence before investing.
- Competition from Other Blockchains
Ethereum has faced competition from other blockchains called “Ethereum killers.” These rival chains, which include Solana, BNB Chain, and Polkadot, handle transactions faster and with lower fees.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that despite all of its challenges, Ethereum and its vibrant developer community remain very active and continue to push the boundaries of blockchain technology. One way they have done this is by significantly lowering the network’s energy consumption and against all odds.
Ethereum’s Energy Consumption
As mentioned earlier, Ethereum now uses the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to validate blocks on the network. This model is known to consume less processing power and energy.
Unlike PoW, proof-of-stake does not require tedious and highly competitive mining processes to validate new transactions. Instead of miners, validators are responsible for adding new blocks of transactions to the chain. To become a validator, you must stake a minimum of 32 ETH as a solo speaker or any amount of ETH if you join a validation pool.
Now, how much energy does Ethereum consume?
A 2023 report showed that Ethereum consumes approximately 0.0026 terawatt-hours per year (TWh/yr) as against 21 TWh/yr when it was using the proof-of-work mechanism. The report further showed that Ethereum consumes less energy than Bitcoin (149 TWh/yr), gold mining (131 TWh/yr), and video gaming in the United States (34 TWh/yr).
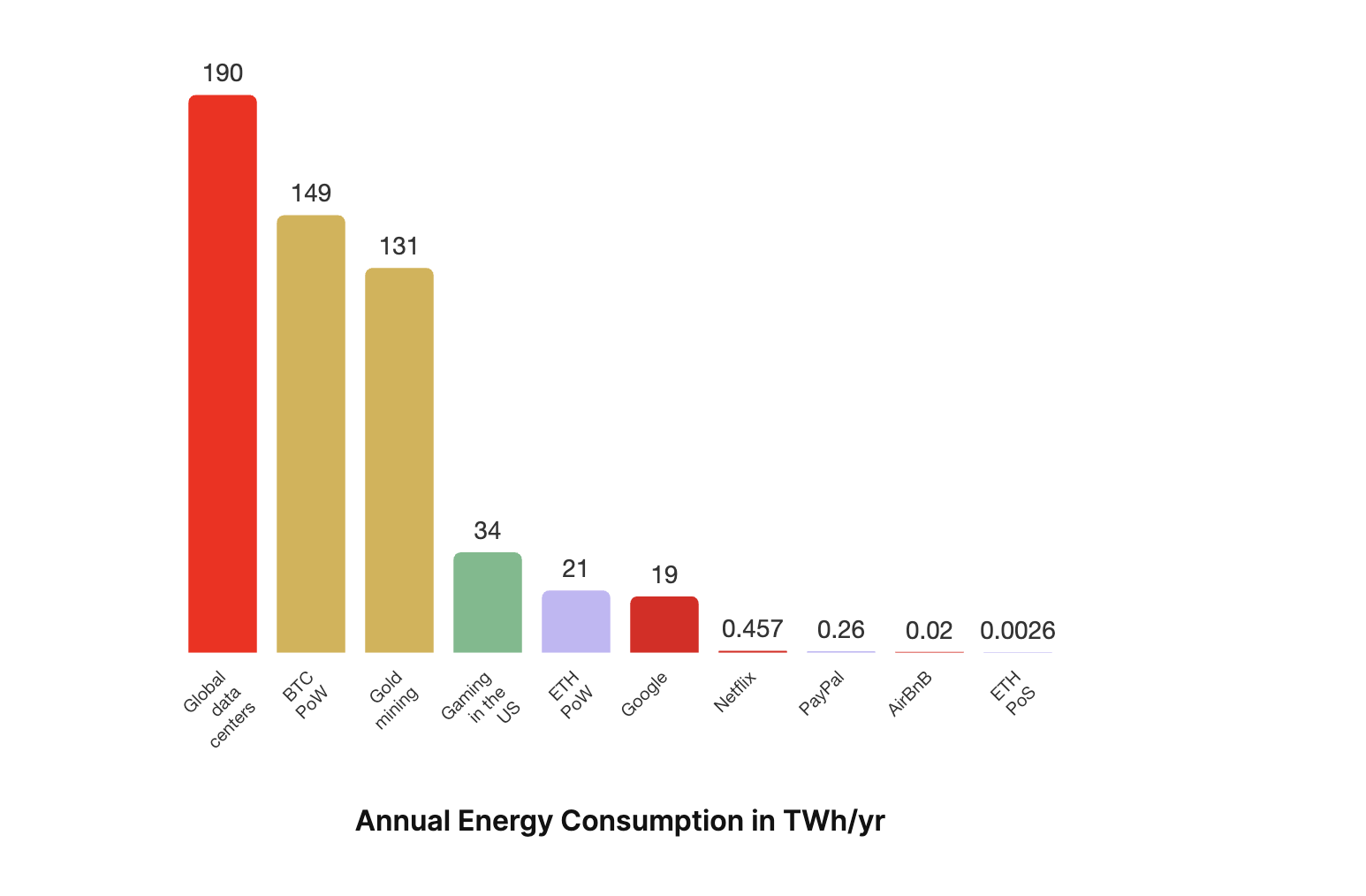
Based on the above data, it is safe to say that the Ethereum network’s goal of switching PoS to ensure the consumption of less energy has been achieved.
Where Can You Buy Ethereum?
You can buy Ethereum on a popular trading platform such as Binance or Coinbase. You can also buy Ethereum on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap or 1inch exchange. The type of exchange you choose depends on your preferences and risk tolerance.
However, It is advisable to select a platform with a simple user interface that supports Ethereum trading pairs. Also, look for platforms with reasonable trading fees and the option to withdraw to a personal wallet.
How to Stake Ethereum
Staking ether (ETH) is locking a certain amount of the cryptocurrency in a smart contract and offering your services to the network as a validator. There are three ways to do this namely:
- Solo Staking
In this method, participants will need 32 ETH to stake and have a dedicated computer with a reliable and constant connection.
This is considered the most secure option as it provides full participation rewards, improves the decentralization of the network, and never requires trusting anyone else with your funds. The network randomly chooses validators to verify transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
- Liquid Staking pools
This method is a collaborative approach that allows many people with smaller amounts of ETH to obtain the 32 ETH required to activate a set of validator keys.
Rewards are distributed based on the pool rules, most of which are based on how much you stake. Some pools, such as Lido, lock your ETH in a smart contract and offer you an ERC-20 token that represents it or this value.
Other pools may not involve smart contracts and are instead mediated off-chain.
- Staking-as-a-service (SaaS)
This option allows you to delegate your ETH to a service provider to do the work and trust that they’ll act in your best interests. This method of staking requires a certain level of trust in the provider. To limit counterparty risk, the keys to withdraw your ETH are usually kept in your possession.
How to invest in Ethereum
By reading this article on what is Ethereum, you have completed the first step to investing in the asset. After all, as the popular saying goes, “If it is worth investing in, then it is also worth taking some time to understand.”
With that first step out of the way, let’s consider exactly how you can invest in Ethereum.
Choose a Trading Platform: One of the easiest ways to invest in Ethereum is by buying ETH on a cryptocurrency exchange. In this case, you can look up the most popular credible exchanges in the country where you live and sign up with them. In most countries, either Binance or Coinbase is available. Other popular options include Kraken, OKX, and Bitget.
Create an Account: Once you decide on a trading platform that fits your needs, the next step in buying Ethereum is to create an account. You will need to provide your name, address, social security number, specified forms of identification, and more.
Verifying the account is usually the final step in the account opening process. Most exchanges require that you verify your account in one or more ways. This is where you will likely need to upload documents to verify your identity and ensure that your account passes regulatory muster. Verification can take anywhere from one hour to a day or two, depending on the exchange.
Deposit Currency: The next step is to deposit currency into your account to make an Ethereum purchase. For centralized platforms, this can be relatively easy after verifying your payment information. Simply add money through your bank account or debit card.
Depositing currency in DEXs can be slightly more difficult. These exchanges require you to send cryptocurrency from your wallet to another. Ethereum and USDT are popular depositing currencies for many DEX platforms so holding large amounts can be beneficial if you’re going to be doing a lot of trading.
Purchase or Trade: Once your account is verified and your money is deposited, you’ll be able to begin purchasing or trading Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies through the exchange.
Each exchange’s interface works somewhat differently. However, they typically involve swapping from your local currency to ETH using a “Convert” feature or an order book. You can read educational guides provided by the exchange for a step-by-step guide for buying ETH on their platform.
Withdraw and store your ETH: Once you have purchased ETH through an exchange, you can withdraw the cryptocurrency to a wallet you control. If you hold a substantial amount, you may choose to invest in a hardware wallet. For smaller investors, a mobile wallet such as Trust Wallet or Metamask might suffice.
Frequently Asked Questions?
Is Ether a Good Investment?
Whether ETH is a good investment depends on your outlook. Like any financial investment, Ethereum comes with its own set of inherent risks despite the growth potential. Investors need to conduct due diligence and only invest money they can afford to lose.
What is the gas fee in Ethereum?
A gas fee is the payment required to successfully conduct a transaction or execute a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain platform. It is similar to the fee you pay when you transfer money from a bank account.
In this case, though, gas fees are paid in Ether (ETH), Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, but are quoted in gwei, a smaller unit of ETH. One gwei is equal to one billionth of an ETH.
Is Ethereum as secure as Bitcoin?
While both Bitcoin and Ethereum are highly secure thanks to encryption and blockchain technology, they take different approaches to achieving security.
Bitcoin relies on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, where miners solve complex puzzles to validate transactions. Ethereum uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they “stake” as collateral.
What is Ethereum Classic?
Ethereum Classic is an open-source, decentralized blockchain platform that emerged following a dispute within the Ethereum community over how to address the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) hack that happened in 2016.
The dispute led to a hard fork of the Ethereum blockchain, with the original blockchain remaining intact as Ethereum Classic and the new blockchain being known as Ethereum (ETH).
Ethereum Classic has a separate community and supports its ecosystem of developers and users. Its native token is ETC.
Can Ethereum transactions be traced?
Yes, Ethereum transactions can be traced using public transaction records on the blockchain, but identifying the actual owner often requires additional information.
What was Ethereum’s all-time high?
As of the time of writing, Ethereum saw its all-time high of $4,878 in November 2021.
Can I mine Ethereum?
Ethereum mining is no longer possible; in 2022, Ethereum moved into a PoS algorithm, rendering mining obsolete. However, Ethereum Classic still supports mining and can be profitable with a high-end graphics card or Ethash ASIC miner.
Conclusion
As you have learned in this guide about Ethereum, the network’s invention in 2015 was a landmark moment for the cryptocurrency industry. Since then, it has grown into one of the most widely used blockchains in the world.
Strong competition has undoubtedly emerged in the form of other networks such as Solana, BNB Chain, and Avalanche. However, Ethereum continues to maintain the upper hand and may continue to do so for a considerable period.
Either way, a rounded-up knowledge of Ethereum, such as the one provided in this Ethereum guide, will no doubt equip you to make an informed decision about investing in Ethereum. Continue to read Cointab, as well, to stay up to date with the latest Ethereum news and developments.
