The Bitcoin halving is one of the most widely anticipated and important events in the cryptocurrency world. It happens every four years and exerts a strong impact on not just the world’s most popular cryptocurrency but also the broader crypto market.
For anyone who has never lived the experience of investing in Bitcoin around the halving, it can be relatively difficult to understand the significance of the event and its impact on the market. However, having the knowledge can also enable investors to make informed decisions on their portfolios.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Bitcoin halving, its history, and its importance.
Bitcoin Halving Explained
The Bitcoin halving is a pre-programmed event that occurs approximately every four years on the network. It involves a line of code in the Bitcoin protocol that reduces the number of coins distributed to miners as a reward for processing transactions on the network.
During the halving, the number of rewards that miners receive is cut in half, effectively reducing the number of new coins entering into circulation. With the lower supply of coins, Bitcoin becomes scarcer, potentially boosting the value of existing coins.
Let us dive a bit deeper into the technical side of how all of this works.
The Bitcoin network uses a consensus algorithm called the Proof-of-Work (PoW) model. Under this model, entities known as miners validate blocks packed with transactions awaiting confirmation in a process called mining and earn BTC rewards.
To secure Bitcoin rewards, miners use specially equipped computers that solve mathematical problems to create new blocks as part of the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism, releasing new coins into circulation and receiving rewards. While blocks of transactions are added approximately every 10 minutes, this timeframe can vary.
When Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of the leading cryptocurrency, introduced the Bitcoin protocol, miners were initially awarded 50 BTC for each block discovered, up until November 28, 2012, when the first halving took place.
The supply has been continuously reduced by half every four years since then. Currently (as of early April 2024), miners earn 6.25 newly created bitcoins when they successfully discover a block and validate the held transfers, in addition to collecting transaction fees from each transfer processed.
At this point, it may appear to how that the Bitcoin halving takes place on a fixed date every four years. However, that is not the case. The Bitcoin software code dictates that the reward for miners is reduced by half after every 210,000 blocks have been added to the blockchain, which is roughly every four years.
With each Bitcoin block taking approximately every 10 minutes to mine, the 210,000 block coincides with the four-year timeline. Hence, the algorithm dictates when the required block is reached, and then it executes the halving to decrease the number of new coins entering the Bitcoin network, thereby combating inflation.
Why Does Bitcoin Halving Matter?
On the surface, Bitcoin halving appears like a mechanism to simply reduce what miners earn. However, the process is designed to control the supply of new bitcoins and ensure that the total supply of bitcoins is finite.
By reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are generated, halving slows down the creation of new coins without reducing the demand, thereby curbing inflation. This scarcity model is inspired by traditional precious metals like gold, where scarcity contributes to their value.
But unlike these assets, we can calculate and predict how the supply decreases over time and how much Bitcoin is still available to mine. The halving is an important mechanism for ensuring Bitcoin’s long-term viability and value as a decentralized digital currency.
Unlike the available supply of fiat currencies, which rises and falls under the watchful eyes of the government, the total supply of Bitcoin is fixed and immutable to avoid devaluation by the arbitrary issuance of new Bitcoin.
Recall that in situations of economic struggle, central banks often bolstered their local economies worldwide by flooding the financial system with newly minted fiat currency. For instance, more than one-fifth of all US Dollars in circulation were created in 2020 alone during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The measure was taken to keep the global economy from collapsing. However, it has had long-term effects like rising inflation, which has impacted many economies around the world. The increased money printing also caused many to doubt the value of their local currency, as it seemingly was created out of thin air.
On the other hand, data shows Bitcoin has a low inflation rate when compared to certain countries. For example, Australia recorded a 4.1% annual inflation in 2023, while the crypto asset has an inflation rate of less than 2%, which is expected to decrease with further halvings.
The above figure shows that Bitcoin’s production scarcity was designed to have a positive impact on the price, making it alluring to investors. In stark contrast to Bitcoin’s halving block reward, the supply of the dollar has roughly tripled since 2000.

Rounding up on this part, Bitcoin’s monetary policy is different from fiat currencies thanks to its limited supply and issuance mechanism, which is written into code shared across the network. There will only ever be 21 million bitcoins. Presently, over 19.66 million bitcoins have already been mined, leaving just under 1.4 million before the full 21 million have been brought into circulation.
Changing the currency’s issuance dynamics would require an immense output of coordination and agreement across the community of Bitcoin users. The same can not be said of modern financial systems, where central banks control the money supply.
Bitcoin Price Halving History
Since its creation in 2009, the leading cryptocurrency has seen three halvings so far, which we can look to as precedents. The first event took place in November 2012 dropping the mining reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC per block.
The second halving took place four years later, in July 2016, reducing the reward to 12.5 bitcoins. The most recent, which took place on May 11, 2020, saw the block reward decrease to the current rate of 6.25 bitcoins.
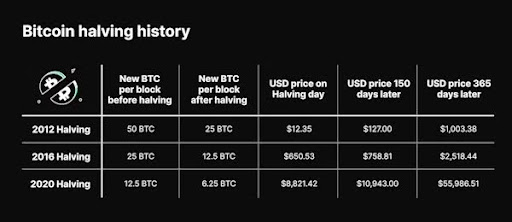
At the time of writing this article, the clock is ticking towards the upcoming halving event, which will likely occur on April 20, 2024, when the block height will reach 840,000. Then, the reward will halve from 6.25 bitcoins to 3.125 bitcoins per block.
The last halving is expected to occur in 2140, when there will be 21 million BTC in circulation, and no more coins will be created. From then, miners will just earn transaction fees paid by users transacting on the blockchain.
There are usually expectations that Bitcoin will see a price jump around the time of halving although it is not guaranteed. This is because of the theory of supply and demand, which says that an item’s price increases when there’s a limited supply of that item and decreases when there is a supply surplus.
Therefore, bitcoin’s halving is expected to decrease the supply of new coins, the theory suggests that demand for Bitcoin should remain stable or increase, potentially leading to upward pressure on its price.
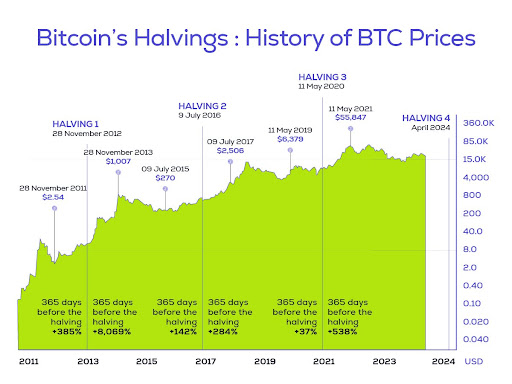
Consequently, a look at past halving shows that the events had a positive impact on the market price, although it took some time. For example, the 2012 halving saw the price of 1 BTC rise by 8,069% in the year following the event.
After the second halving in July 2016, the price increased by about 40% from $650 to $20,000 in December 2017. The last halving, which took place in May 2020, took BTC to an all-time high (ATH) of around $69,000.
Therefore, many in the crypto world speculate that the 2024 halving will mirror a similar pattern: a temporary dip in Bitcoin’s price followed by a resurgence that may even surpass its former all-time high.
Market experts predict that BTC will reach as high as $200,000 or more after the halving occurs. The forecast comes after the approval of the spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in the United States, which has contributed significantly to the BTC price increase. Therefore, one might wonder if the market will be favorable now.
Should I Buy Bitcoin Before Halving?
The Bitcoin halving, as discussed so far, has historically led to a new all-time high in price. Therefore, many experienced investors consider it a good idea to buy Bitcoin either before the halving event or shortly after.
However, it is important to understand that past performances are not a guarantee of future results, and market dynamics may also differ.
For instance, the 2020 Bitcoin halving coincided with COVID-19 and global lockdowns. Meanwhile, the 2024 cycle will come just a few months after the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the launch of the spot Bitcoin ETF products. The move unlocked BTC to a wealth of institutional capital and helped its price to reach a new all-time high before halving for the first time in its history.
Therefore, just like every other time, investors are advised to conduct due diligence, bearing in mind that halving is just one of many factors that have influenced Bitcoin’s price since its creation.
Additionally, investors must be cautious about halving expectations because although scarcity is expected to drive price appreciation, reduced mining activity could cause the price to level off. The focus should be on the network’s overall growth, as its development will likely fulfill its potential as a global store of value.
Final Words
The Bitcoin halving is considered one of Bitcoin’s unique aspects because the block reward is programmed to reduce over time.
Its role in controlling the supply of new Bitcoins is one of the reasons the world’s most popular cryptocurrency is seen as a store of value more akin to gold than a fiat currency. The block reward shows that no central entity can create Bitcoin outside of the strict schedule, making it a highly valuable digital asset.
